The interest in Non-fungible Tokens (NFTs) has ‘exploded’ recently, but it is not clear what final form they will take. This innovation will have difficulties reaching a wider audience until more clarity is achieved on two main issues: What exactly are the NFT business models, and how do they build trust. The findings of recent research (Zarifis and Cheng, 2022), illustrated in figure 1, show that there are four NFT business models:
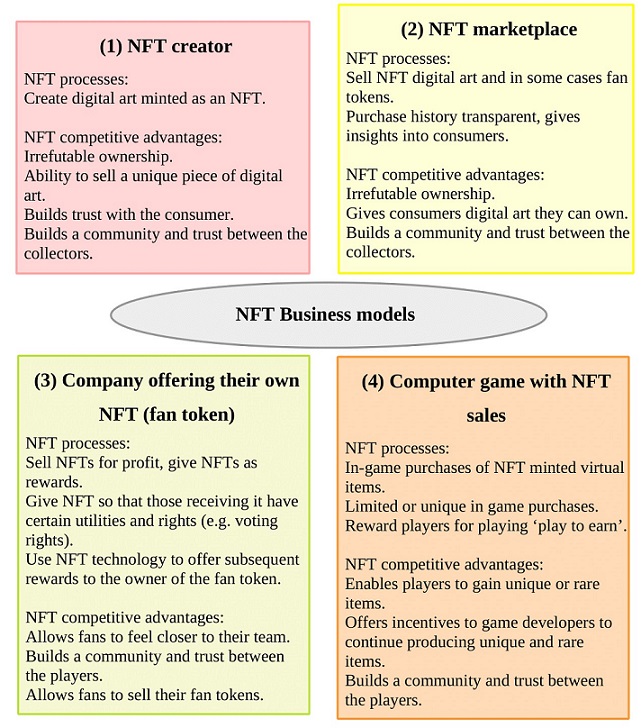
(1) The first business model is an NFT creator: They can create digital art that is then minted as an NFT, and sold on an NFT platform. The NFT competitive advantages include having proof of irrefutable ownership, and the ability to sell a piece of art that is unique or limited to a low number. The reliability and transparency of the NFT, build trust with the consumer.
(2) The second business model is an NFT marketplace, selling creators’ NFTs: The competitive advantage of NFTs as part of this business model is once again the irrefutable ownership, and that it gives consumers digital art they can own. The purchase history of the consumers is transparent, so this gives insights into their interests. As with the previous business model, a community and trust are built between the collectors.
(3) The third business model is a Company offering their own NFT, typically a fan token: This business model has several NFT processes. These are to sell NFTs for profit, to give NFTs as rewards, make payment with fan tokens, give an NFT so that the person receiving it has certain utilities and rights, such as voting rights. The competitive advantages of NFTs, within this business model, are that they allow fans to feel closer to their team and builds a community and trust between the fans.
(4) The fourth business model is a Computer game with NFT sales: There can be in-game purchases of NFT minted virtual items, limited or unique in game purchases and players can be rewarded for playing, know as ‘play to earn’. This offers incentives to game developers to continue producing rare items, provides an ongoing revenue stream for existing games, and builds a community and trust between the players.
Reference
Zarifis A. & Cheng X. (2022) ‘The business models of NFTs and Fan Tokens and how they build trust’, Journal of Electronic Business & Digital Economics, vol.1, pp.1-14. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1108/JEBDE-07-2022-0021